EZG-File
![]() BlueM.Sim | Download | Application | Theory | Development
BlueM.Sim | Download | Application | Theory | Development
Input files · ALL SYS · FKT KTR · EXT JGG WGG TGG · TAL HYA TRS EIN URB VER RUE BEK EZG FKA · BOA BOD LNZ EFL · DIF
Rural catchment
also refer to Theory: Rural catchment
File
*Einzugsgebiete (*.EZG) *====================== *|------|-----|------------------------------|--------|------------------|------------------------|---------|-----|----------|-----|----------------------------------------------|--------------|-------------------------------------|--------------| *| Bez | KNG | Gebietskenngroessen | N | Verdunstung | Temperatur | QBASIS | PSI | SCS (2) | BF0 | Retentionskonstanten | Aufteilung | Schneekonstanten | QSpende | *| | | A VG Ho Hu L | Datei |Kng Sum Datei |Kng Tem JGG TGG Datei | qB JGG | (1) | CN VorRg| (3) | R K(VG) K1 K2 Int Bas nLin Expo| Beta1 Beta2 | R GrT NSchD GrD RateT RateSB | MQ | *|------|-----|------------------------------|--------|------------------|------------------------|---------|-----|----------|-----|----------------------------------------------|--------------|-------------------------------------|--------------| *| - | 1-4 | ha % muNN muNN m | Nummer |1/2 mm/a Nummer |1/2 °C - - Nummer |l/sqkm - | - | - mm | % | - h h h h h J/N - | - - | - °C % % mm/(°d) mm/d | m3/(s ha) | *|-<-->-|-<->-|<----><----><----><----><---->|<------>|-+-<---->-<------>|-+-<-->-<->-<->-<------>|<--->-<->|<--->|<---><--->|<--->|-+-<---->-<---->-<---->-<---->-<---->--+-<--->|-<---->-<---->|-+-<--->-<--->-<--->-<----->-<----->-|-<---------->-| | A | B | C D E F G | H | I J K | L M N O P | Q R | S | T U | V |R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 | B1 B2 |S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 | Q1 | *|------|-----|------------------------------|--------|------------------|------------------------|---------|-----|----------|-----|----------------------------------------------|--------------|-------------------------------------|--------------|
Explanations
Versionen:
- A: unique ID (must begin with 'A'!)
- B: calculation type [1-4] (see below). Refers to the pervious areas; the impervious areas are generally calculated with the same methods.
- C: area [ha]
- D: fraction of impervious area [%]
- E: maximum height [müNN]
- F: minimum height [müNN]
- G: longest flow path [m]
Rainfall:
- H: Filenumber of the rainfall file (refer to *.EXT-File)
Evaporation:
- I: calculation type for the evaporation (1 = annual evaporation; 2 = evaporation out of a time series / file)
- J: annual evaporation [mm/a]
- If soil moisture calculation: the sum referring to grassland must be entered,which is internally overprinted with hydrographs according to Brandt[1] and Haude[2][3] and is adjusted to the land use in the individual hydrological response unit.
- K: filenumber of the evaporation time series to be utilized (refer to *.EXT-File)
- only daily values may be listed in the time series because the time series values are always additionally overprinted with a daily pattern! (Bug 1)
Temperature:
- L: calculation type for the temperature (1 = mean value with optional annual/ weekly/ daily pattern; 2 = temperature out of a time series/ file)
- M: mean temperature [°C]
- N, O: number of the annual/ weekly/ daily pattern to be utilized
- P: filenumber of the temperature time series to be utilized (refer to *.EXT-File)
Base flow:
- Q: constant base flow [l/s.km²]
- If soil moisture calculation this value only surves the purpose of calculating the initial reservoir content of the groundwater and interflow reservoirs:
S0,Basis = QB,0 × KBasisS0,Interflow = QB,0 × KInterflow
- R: number of the annual pattern to be utilized to scale the base flow (not used by soil moisture)
Calculation type 1: run-off coefficient method:
- S: run-off coefficient
(0 < ψ ≤ 1)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \psi = \frac{N_{eff} + E_T + h_v}{N} }[/math]
- with:
Neff=effective rainfallET= evaporationhv= initial losses (losses due to wetting and troughs)- also refer to http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abflussbeiwert
Calculation type 2: SCS-Method:
- refer to Theory:SCS-Method
- T: CN-Value
(0 < CN ≤ 100) - U: 21-Day prior rainfall height [mm] (is distributed evenly over 21 days), only relevant for the period before the simulation, during the simulation, the prior rainfall height is continuously simulated.
Calculation type 3: soil moisture calculation:
- refer to Theory: soil moisture calculation
- V: initial soil moisture [% of field capacity] this value is overprinted by the global initial soil moisture specified in the ALL-File.
Calculation type 4: specific discharge:
- Q1: constant specific discharge [m3/(s ha)]
Retention constant:
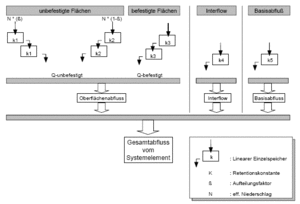
- R1: manual input of the retention constants as well as the distribution factors [Y/N]
- if No (
N) the retention constants for the surface runoff (R2, R3 and R4) as well as the distribution factors (B1 and B2) are calculated internally according to Zaiß[4] on the basis of catchment characteristics. The calculated parameters are written into the Protocol-File, if it is activated.
- if No (
- R2: Retention constant of the impervious area cascade [h]
- R3: Retention constant of the fast cascade [h]
- R4: Retention constant of the slow cascade [h]
- R5: Retention constant of interflow [h] (only for soil moisture calculation)
- R6: Retention constant of base flow [h] (only for soil moisture calculation)
- R7: non-linear calculation [Y/N]
- R8: Exponent fot the non-linear calculation
Distribution factors:
The distribution factors Beta1 and Beta2 only refer to pervious areas!
The sum of Beta1 and Beta2 must be 1 (β1 + β2 = 1)!
- B1: Distribution factor of the fast cascade
0 ≤ β1 ≤ 1 - B2: Distribution factor of the slow cascade
0 ≤ β2 ≤ 1
The distribution factor β3 of the cascade for impervious areas is determined internally on basis of the fraction of impervious areas (D).
- Hint
- Providing
β2is optional. If not provided it is calculated byβ2 = 1. - β1
Snow constants:
For the calculation of snow the Snow-Compaction Method according to Knauf[5] is applied.
- S1: manual input of the snow constants [Y/N]
- (if
Nor emtpy, default values will be utilized)
- (if
- S2: Threshold temperature for the formation of snow [°C]
- S3: New-snow density [%]
- S4: Threshold density as of which water output begins [%]
- S5: Temperature dependent melting rate [mm/(K×d)]
- S6: Insolation and soil warmth dependent melting rate [mm/d]
Value ranges and default values:
| Parameter | Unit | Default value | Value range[5] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold temperature | °C | 0 | ? |
| New-snow density | % | 11 | 5 - 20 |
| Threshold density | % | 40 | 40 - 45 |
| Temperature dependent melting rate | mm/(K×d) | 1.8 | ? |
| Insolation and soil warmth dependent melting rate | mm/d | 4.2 | ? |
Specific discharge:
constant specific discharge (calculation type = 4)
- Q1: constant specific discharge [m3/(s ha)]
Literature
- ↑ Brandt, T. (1979): Modell zur Abflussgangliniensimulation unter Berücksichtigung des grundwasserbürtigen Abflusses, Technischer Bericht Nr. 24 aus dem Institut für Wasserbau, Fachgebiet Ingenieurhydrologie und Hydraulik der TH Darmstadt
- ↑ Haude, W. (1954): Zur praktischen Bestimmung der aktuellen und potentiellen Evapotranspiration. – Mitteilungen des DWD, Bd. 8; Bad Kissingen
- ↑ Haude, W. (1955): Zur Bestimmung der Verdunstung auf möglichst einfache Weise. Mitteilungen des DWD, 2 (11), Bad Kissingen
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Zaiß, H. (1986): Abflussermittlung aus Teilflächen, in "Hydrologische Abflussmodelle in der praktischen Anwendung", 36. Fortbildungslehrgang des BWK-Hessen am 21. März 1986, Friedberg [ihwb-Bibliothek: Inv.-Nr. 5593, 10 BWK 36] PDF
 OCR
OCR 
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Knauf, D. (1980): Die Berechnung des Abflusses aus einer Schneedecke, in: DVWK-Schriften, Heft 46, Analyse und Berechnung oberirdischer Abflüsse PDF