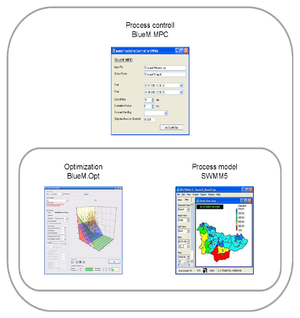
BlueM.MPC application
BlueM.MPC is a modular software consisting of three modules. The supervising module BlueM.MPC coordinates work and data flow. Module SWMM5 represents the process model which is used for the evaluation of the objective function that is required by the optimization module BlueM.Opt. Data exchange between modules is based on text files.
Dataset
Application of BlueM.MPC requires seven input files:
Process control:
- XML-File: Inflow prediction
Optimization:
- OPT-Datei: Definition of optimization parameters
- ZIE-Datei: Definition of objective function
- MOD-Datei: Localization / identification of optimzation parameters in inp
Process model:
- INP-File: Definition of the process model
- TXT-File: Inflow-Data
- HSF-File: Initial flows and water levels
Simulation
After starting the application MPC.exe a user form is opened. In this form all relevant information for the process control has to be filled in. After pressing the button Init BlueM.Opt the GUI of the optimizer BlueM.Opt is launched. The user selects an optimization algorithm and after setting the relevant optimization parameters the MPC simulation will start from there.
The following informations are required in the BlueM.MPC form:
- Input File. Path and file name of the process model (INP-File).
- Output Folder. Path of the folder for results and log-files.
- Start. Date and time of the start of the MPC simulations.
- Stop. Datum und Uhrzeit des Endzeitpunkts für die modellprädiktive Steuerung.
- Control step. Größe des Steuerungszeitschritts in Minuten.
- Evaluation horizon. Größe des Evaluierungshorizonts in Stunden.
- Forecast handling. Auswahl der Methode, mit der ermittelt wird, wie der Zeitdifferenz zwischen Vorhersagehorizont und Evaluierungshorizont umgegangen werden soll (siehe Abbildung 3.3). Der Benutzer kann derzeit zwischen drei Methoden wählen: (1) Alle Zuflusswerte zu Null setzen, (2) Mittelwerte des Vorhersagehorizonts ansetzen oder (3) den letzten Wert des Vorhersagehorizonts verwenden.
- Objective function threshold. Optionaler Wert, wenn Zielfunktionswerte gegen den Wert Null minimiert werden (z.B. bei der Minimierung der Entlastungsabflüsse), um die exzessiven Rechenzeiten bei den Simulationsstudien zu vermindern. Es kann ein Schwellwert eingegeben werden, mit dem der berechnete Zielfunktionswert des ersten Simulationslaufs verglichen wird. Ist der Zielfunktionswert kleiner als der Schwellwert, wird die Iteration nicht durchgeführt.